Unsure if your business has adequate layered security for your digital assets? Read on because today, we'll cover precisely what layered security looks like and how you can achieve it.
Welcome to another Westway IT guide!
What is layered security?
In 2023, security breaches cost businesses an average of £1,100 per incident in the UK. According to a government survey, the cost increased to £4,960 for medium to larger enterprises. At the same time, cyber hygiene fell to 60-70%, leaving hackers with increasing opportunities to target businesses like yours.
Layered security is a comprehensive approach to safeguarding your business against digital threats. It works by implementing multiple overlapping security measures at different levels of your IT infrastructure.
The concept of multiple overlapping layers is deceptively simple yet extraordinarily effective. It's the idea that relying on a single solution, like an antivirus program, cannot protect your business alone. Just as a bank doesn't secure its vault with just one lock, your digital assets require a multifaceted approach to guard against cyber threats.
Typically, our approach to layered security is three-fold.
The 3 essential elements of your layered security policy
If you consider each element makes the side of a triangle, that will look something like this.
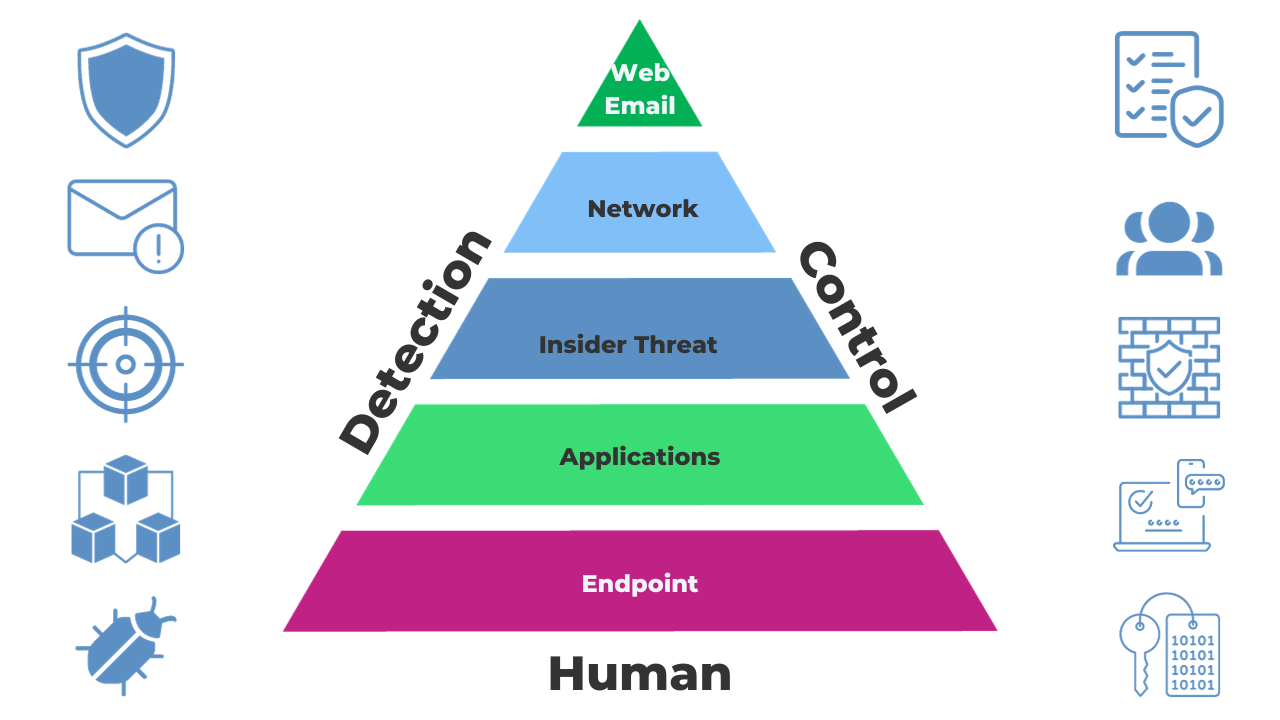
1. Detection
At the core of layered security lies your capability to detect when something suspicious happens within your digital environment. This is your early warning system. Think of it as the watchful eye that spots intruders at the gate.
Detection involves using tools and technologies to monitor network traffic, system logs, and user behaviours. The objective is identifying unusual or suspicious activities that could suggest a security breach.
Detection mechanisms include:
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) monitor network traffic for signs of unauthorised access or malicious activity. When suspicious patterns are detected, alarms are raised.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools aggregate and analyse log data from various sources, providing a comprehensive view of your network's security. They can identify patterns that may indicate a breach.
- Behavioural analytics use machine learning algorithms to establish a "normal" behaviour baseline for your network and users. Any deviation from this baseline triggers alerts.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions monitor individual devices (endpoints) for signs of suspicious activity. They can help identify and contain threats at the device level.
Effective detection ensures that you are aware of potential threats as soon as they arise, allowing for a swift and targeted response.
2. Control
Controlling what abilities individuals and entities have within your system is critical. It involves limiting access, monitoring privileges, and enforcing data protection policies.
Control mechanisms include:
- Access controls define who can access specific resources or areas within your network. Examples include password-protected folders and role-based access controls (RBAC).
- Privileged Access Management (PAM) solutions restrict and monitor access to sensitive systems and data. They ensure that only authorised personnel can make critical changes.
- Application Whitelisting allows you to specify which applications can run on your network. This prevents the execution of unauthorised or potentially harmful software.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) focuses on preventing data leakage by monitoring and controlling the movement of sensitive data within and outside the organisation.
Control mechanisms are about setting rules, boundaries, and permissions to maintain the integrity of your digital assets.
3. Human
Your employees play a pivotal role. They can identify irregular activities, report potential threats, and follow security protocols. Their vigilance and awareness can make or break your security.
Employees can:
- Spot phishing attempts - Educated employees are less likely to fall for phishing emails and report them quickly.
- Report suspicious activity - When employees understand unusual behaviour, they can report it promptly.
- Follow security protocols - Ensuring employees adhere to security policies and procedures is essential. They are the first line of defence in safeguarding your digital assets.
Okay, so we have our triangle. Within these 3 elements are 5 overlapping layers.
The 5 levels of layered security
1. Internet (web/email)
This is the top layer and first line of defence, facing the vast expanse of the internet. Essential security measures at this level include:
- Firewalls act as gatekeepers, monitoring and controlling traffic between your network and the internet. They are your first line of defence against external threats.
- Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) actively identify and block potential threats like network-based attacks and vulnerabilities.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) encrypt communication between remote users and your network, safeguarding data in transit.
2. Internal network
Within your network, further security measures protect the information and resources you've built from outside attacks. These include:
- Network segmentation - Dividing your network into smaller, isolated segments enhances security by limiting lateral movement for potential attackers.
- Access controls - Enforcing access controls ensures that only authorised users can access specific resources, reducing the risk of unauthorised access.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS) - These systems monitor internal network traffic for signs of suspicious activity or breaches.
3. Insider threats
This level is particularly significant because it addresses the risks that originate from within your organisation. Measures include:
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA)- These monitor user and entity behaviour to identify deviations from the norm, helping to spot insider threats.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) - These help protect against accidental and malicious data leaks, providing visibility and control over sensitive data.
- Employee training - Educating employees about security and recognising insider threats is essential to mitigating these risks.
4. Applications
To prevent vulnerabilities and breaches, your software and services must be fortified. Critical security measures here include:
- Secure development practices ensure that applications are developed with security to reduce exposures.
- Regular patching and updates keep all applications up-to-date.
- Application firewalls protect web applications from threats, including cross-site scripting and SQL injection attacks.
5. Endpoint (PC)
Every device, from PCs to mobile phones, is a potential entry point for cyber threats. Securing these endpoints is paramount, and measures include:
- Antivirus and Antimalware - While not the sole solution, antivirus and antimalware software remain a crucial layer of protection.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) - EDR solutions monitor individual devices for signs of suspicious activity and can help contain threats.
- Mobile Device Management (MDM) - MDM solutions offer control and security for mobile devices used within the organisation.
The connection between IT security and business resilience
Business resilience refers to your ability to withstand disruptions and adapt to change. Your IT security is intrinsically linked to business resilience for several reasons:
- Risk mitigation - IT security measures reduce the likelihood and impact of security incidents, helping your business adapt and recover more effectively from disruptions.
- Cost savings - The cost of recovering from a security breach outstrips the cost of implementing strong security measures.
- Client relations - A security breach can destroy customer trust and tarnish your brand.
- Loss of intellectual property - Intellectual property theft can have long-lasting impacts on your organisation's competitiveness.
- Legal and regulatory compliance - Many industries are subject to strict regulations related to data protection. Non-compliance can result in legal consequences, making IT security a necessity and a legal obligation.
The role of managed IT services in your layered security
For some businesses, managing layered security in-house can be a complex task. Dedicated managed security service providers (MSSPs) offer a viable solution. They specialise in securing businesses and can tailor a layered security strategy to your needs.
If you are a smaller business, you will be looking for reliable managed IT services, just as we offer at Westway IT. Managed IT solutions cater for your security needs alongside other beneficial IT services, like hardware and software management and IT helpdesks.
Getting the right help can make all the difference as you maintain and grow your business, especially in securing your assets.
Need a chat about your layered security and business resilience? Book a 15-minute video call with John today!
